Technisches Handbuch für Schrittmotoren
Stand: Mai 2018
Ein „Motor“ ist ein Gerät, das elektrische Energie in mechanische Leistung umwandelt und erforderlich ist, wenn man etwas bewegen oder abbremsen möchte. Ein Schrittmotor ist eine spezielle Motorart, die insbesondere für präzise Positionierungen geeignet ist.Dieses technische Handbuch erklärt den Aufbau, das Rotationsprinzip und verschiedene Eigenschaften, damit Sie die Hybrid-Schrittmotoren verstehen und effektiv nutzen können.
Table of Contents
Preface: History of Stepper Motors
-
1. Features of Stepper Motors
- 1.1. Movement of Stepper Motor
- 1.2. Positioning with High Resolution and High Accuracy
- 1.3. Rotation Amount and Number of Pulses are Proportional
- 1.4. Rotation Speed and Pulse Speed are Proportional
- 1.5. Position Holding at Standstill State
- 1.6. High Synchronization Performance
-
2. Stepper Motor Types
- 2.1. PM Type Stepper Motor
- 2.2. VR Type Stepper Motor
- 2.3. Hybrid Type Stepper Motor
-
3. Structure and Principle of Operation for Hybrid Type Stepper Motor
- 3.1. Structure of Hybrid Type Stepper Motor
- 3.2. Generation of Holding Force
- 3.3. Teeth Arrange Offset and Step-like Movement
- 3.4. Step Angle
- 3.5. 5-Phase Stepper Motor
-
4. Characteristics of Stepper Motors
- 4.1. Static Characteristics
- 4.2. Transient Characteristics
- 4.3. Dynamic Characteristics
- 4.4. Temperature Characteristics
- 4.5. Noise Characteristics
-
5. Drive Circuit
- 5.1. Wiring Method
- 5.2. Excitation Mode and Excitation Sequence
- 5.3. Drive System
- 5.4. Microstep Drive
- 5.5. New Driving Method
-
6. Types and Features of Controllers
- 6.1. Operation Methods of Stepper Motors
- 6.2. Types of Controllers
- 6.3. Network Control of Stepper Motors
-
7. Theory of Stepper Motors
- 7.1. Dynamics of a Rotating Body
- 7.2. Back EMF and Torque
- 7.3. Description in d-q Coordinate of a Stepper Motor
- Message from Author
Für den vollständigen Text laden Sie bitte das PDF herunter.
1. Features of Stepper Motors
A stepper motor can rotate at a precise rotation speed and stop at an accurate position without using a position feedback device or a brake. This makes a positioning system possible to configure easily.
1.1. Movement of Stepper Motor
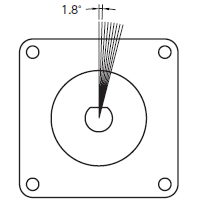
A motor is a device to perform continuous rotation, but a stepper motor can achieve precise operation without using a feedback device. It rotates at a specified angle every time a pulse signal is input to a driving circuit (driver).
The stepper motor moves as if continuous rotation is performed when the pulse signal is fast, but it intermittently rotates like the movement of the second hand of the analog clock when the pulse signal is slow. For example, in the case of a 2-phase stepper motor, the basic movement is 1.8° per step as shown in the Fig. 1.1.
Den vollständigen Text können Sie als PDF herunterladen.