Selecting a Motor: Selection Example - Pulley Mechanism
For AC Motors
(1) Specifications and Operation Conditions of the Drive Mechanism
The following is an example of how to select an induction motor to drive a belt conveyor:
A motor must be selected that meets the following required specifications.
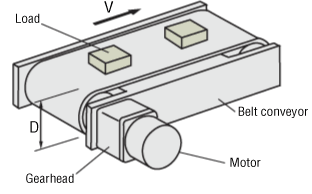
- Total Mass of Belt and Load
- m1 = 25 [kg]
- External Force
- F A = 0 [N]
- Friction Coefficient of Sliding Surface
- μ = 0.3
- Roller Diameter
- D = 90 [mm]
- Roller Mass
- m2 = 1 [kg]
- Belt and Roller Efficiency
- η = 0.9
- Belt Speed
- V = 180 [mm/s] ± 10 %
- Motor Power Supply
- Single-Phase 100 VAC 50 Hz
- Operating Time
- 8 hours of operation per day
(2) Determine the Gear Ratio of Gearhead
Since the rated speed for an induction motor (4-pole) at 50 Hz is 1200~1300 [r/min], select a gearhead gear ratio within this range.
Select a gear ratio of i = 36 from within this range.
(3) Calculate the Required Torque TM [N·m]
Consider the safety factor Sf = 2.
Select a gearhead and induction motor that satisfy the permissible torque for the gearhead with the calculation results so far (gear ratio i = 36, load torque TL = 7.36 [N·m]) as the conditions.
Here, 5IK40GN-AW2J and 5GN36K are tentatively selected as the motor and gearhead respectively by referring to the specifications.
Convert this load torque to a value on the motor output shaft to obtain the required torque TM.
(Transmission efficiency of gearhead 5GN36K ηG = 0.73)
The starting torque of the previously selected 5IK40GN-AW2J motor is 200 [mN·m], which does not satisfy the required torque.
Therefore, we will change the motor to one size up, 5IK60GE-AW2J, and the gearhead to 5GE36S. In this case, the formula is as follows.
(transmission efficiency of gearhead 5GE36S ηG=0.66)
The starting torque of the 5IK60GE-AW2J motor is 320 [mN·m], which satisfies the required torque of 310 [mN·m].
(4) Check the Load Inertia J [kg·m2]
Inertia of belt and load
Inertia of roller
Calculate the load inertia for the gearhead output shaft J.
Take into account that there are 2 rollers (Jm2).
Here, permissible load inertia of gearhead 5GE36S (gear ratio 36) JG is given by the following formula.
Therefore, J < JG, the load inertia is less than the permissible value and there is no problem. Since the motor selected has a rated torque of 490 [mN·m], which is larger than the actual load torque, the motor will operate at a higher rotation speed than the rated speed.
Therefore, use the rotation speed with no load (approx. 1470 r/min) to calculate belt speed, and confirm whether the selected product meets the specifications.
This confirms that the motor meets the specifications.
Based on the above, 5IK60GE-AW2J, and 5GE36S are selected as the motor and gearhead respectively.
For Low-Speed Synchronous Motors SMK Series
(1) Specifications and Operation Conditions of the Drive Mechanism
Select the load mass that can be driven by the SMK237A-A motor when the belt drive table shown in figure 1 is driven with an operating pattern as shown in figure 2.
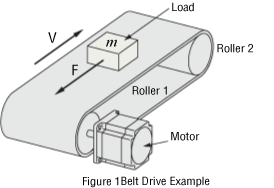
- Total Mass of Belt and Load
- m1 = 1 [kg]
- Roller Diameter
- D = 30 [mm]
- Roller Mass
- m2 = 0.1 [kg]
- Friction Coefficient of Sliding Surface
- μ = 0.04
- Belt and Pulley Efficiency
- η = 0.9
- Power Supply Frequency
- 50 Hz (Rotation Speed: 60 r/min)
Low-speed synchronous motors share the same basic principle with 2-phase stepper motors. Accordingly, the torque is calculated in the same manner as for a 2-phase stepper motors.
(2) Belt Speed V [mm/s]
Check the speed of the belt (load).
(3) Calculate the Load Torque TL [N·m]
(4) Calculate the Load Inertia JL [kg·m2]
Inertia of belt and load
Inertia of roller
Calculate the load inertia JL.
Take into account that there are 2 rollers (Jm2).
(5) Calculate the Acceleration Torque Ta [N·m]
Calculate the self-start acceleration torque.
(6) Calculate the Required Torque TM [N·m] (Safety factor Sf = 2)
(7) Select a Motor
Select a motor that satisfies both the required operation torque and the permissible load inertia.
| Product Name | Rotor Inertia [kg·m2] |
Permissible Load Inertia [kg·m2] |
Output Torque [N·m] |
|---|---|---|---|
| SMK237A-A | 0.3 x 10-4 | 2.5 x 10-4 | 0.37 |
When the required torque is calculated by substituting the rotor inertia, the value obtained is TM = 0.362 [N·m], which is lower than the output torque. Next, check the permissible load inertia. Since the load inertia calculated in (4) is also below the permissible load inertia, SMK237A-A can be used.
For Brushless Motors
(1) Specifications and Operation Conditions of the Drive Mechanism
Select a brushless motor to drive the belt conveyor, as shown in the figure below.
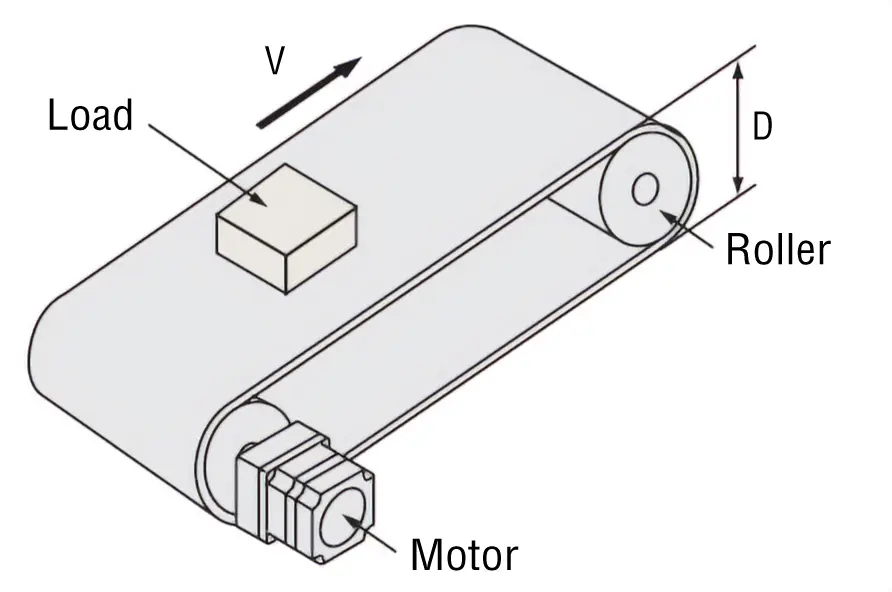
- Belt Speed
- VL = 0.05~1 [m/s]
- Motor Power Supply
- Single-Phase 100 VAC
Belt Conveyor Drive
- Roller Diameter
- D = 0.1 [m]
- Roller Mass
- m2 = 1 [kg]
- Total Mass of Belt and Load
- m1 = 7 [kg]
- External Force
- FA = 0 [N]
- Friction Coefficient of Sliding Surface
- μ = 0.3
- Belt and Roller Efficiency
- η = 0.9
(2) Determine the Rotation Speed Range to be Used
Calculate the roller rotation speed from the belt speed.
For the gearhead gear ratio, select "15" in the speed range 5.4 to 266, ensuring the minimum and maximum rotation speeds are within the speed range in the specifications table.
(3) Calculate the Load Inertia JG [kg·m2]
Inertia of belt and load
Inertia of roller
Calculate the load inertia JG.
Take into account that there are 2 rollers (Jm2).
From the specifications table, the permissible load inertia with output power 120 W and at a gear ratio of 15 is 225 × 10−4 [kg·m2].
(4) Calculate the Load Torque TL [N·m]
Select a brushless motor with an output power of 120 W and a gear ratio of 15 from the specifications table.
Since the permissible torque is 5.2 [N·m], the safety factor is TM/TL = 5.2/1.15 ≒ 4.5.
Generally, a motor can operate at a safety factor of 1.5∼2 or more.