Selecting a Motor: Formula for Inertia J [kg·m2]
Formula for the Inertia
Inertia of a Cylinder
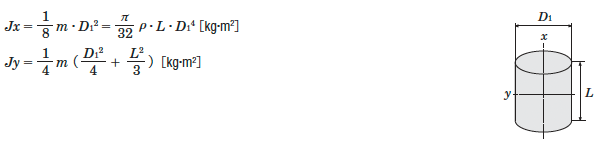
Inertia of a Hollow Cylinder
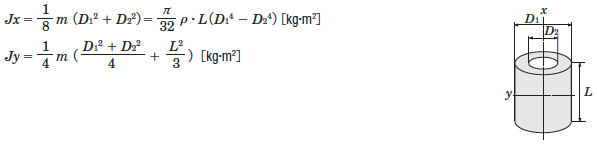
Inertia on Off-Center Axis
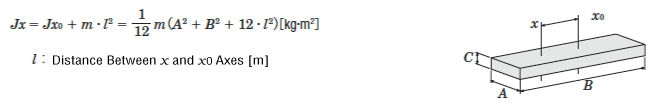
Inertia of a Rectangular Pillar
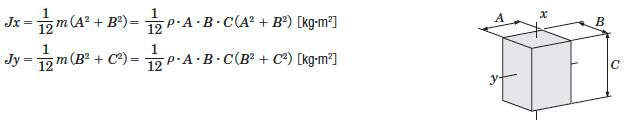
Inertia of an Object in Linear Motion
\(\begin{align}
J=m\left(\frac{A}{2 \pi} \right)^2\ [\mathrm{kg} \cdot \mathrm{m^2}]
\hspace{25pt}{A}: \text{Unit movement}[\mathrm{m/rev}]
\end{align}\)
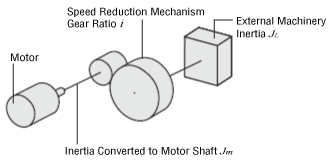
Conversion Formula for the Inertia of the Motor Shaft When Using a Speed Reduction Mechanism
\(\begin{align}
Jm=\frac{1}{i^2} {J_L}
\end{align}\)
Formula for the Relationship Between J and GD2
\(\begin{align}
J=\frac{1}{4} {GD}^2
\end{align}\)
Density
- Stainless Steel (SUS304)
- ρ = 8.0 × 103 [kg/m3]
- Iron
- ρ = 7.9 × 103 [kg/m3]
- Aluminum
- ρ = 2.8 × 103 [kg/m3]
- Brass
- ρ = 8.5 × 103 [kg/m3]
- Nylon
- ρ = 1.1 × 103 [kg/m3]
- Jx
- Inertia on x Axis [kg·m2]
- Jy
- Inertia on y Axis [kg·m2]
- Jx0
- Inertia on x0-Axis (Centered axis) [kg·m2]
- m
- Mass [kg]
- D1
- Outer Diameter [m]
- D2
- Inner Diameter [m]
- ρ
- Density [kg/m3]
- L
- Length [m]