Selecting a Compact Electric Cylinder: DRLII Series
Selection Method
(1) Confirming the Required Specifications
Confirm the required specifications for the equipment.
- Load mass
- m = 5 [kg]
- Positioning Distance
- L = 40 [mm]
- Positioning Time
- T = Within 1.5 seconds
- Drive Direction
- Vertical
- Stopping Accuracy
- ± 0.01 mm
(2) Tentative Selection of Electric Actuators
The following electric actuator is tentatively selected based on the required specifications.
- Product Name
- DRL42G-04A2P-KD
- Lead
- 2 mm
- Types of Ball Screws
- Rolled Ball Screw
- Resolution
- 0.04 mm
- Power Supply Input
- 24 VDC
(3) Confirming the Positioning Time
Check whether the actuator can perform the necessary positioning within the specified time. This can be done by obtaining a rough positioning time from the graph or by obtaining a fairly accurate positioning time by calculation. Each of the confirmation procedures is explained below.
The actual operating time is subject to a small margin of error, so use the calculation only as a reference.
Obtaining From a Graph
- ①
-
Use the graph to confirm the positioning time necessary for a positioning distance of 40 mm.
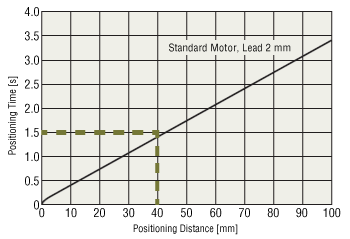
The graph above shows that the load can be positioned over a positioning distance of 40 mm within 1.5 seconds.
- ②
- If the positioning time requirement is not satisfied, select a different model.
Using Formula Calculations
- ①
- Confirm operation conditions
Please check the following conditions:
Positioning distance, starting speed, acceleration, and operating speed
- ②
-
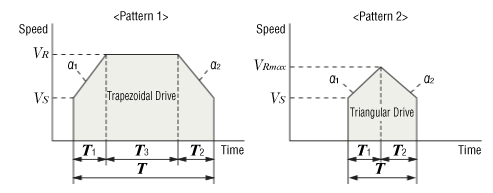
From the operation conditions above, confirm whether the drive pattern is a triangular drive or trapezoidal drive
Calculate the maximum speed of triangular drive from the positioning distance, starting speed, acceleration and operating speed. If the calculated maximum speed is equal to or below the operating speed, the operation is considered a triangular drive. If the maximum speed exceeds the operating speed, the operation is considered a trapezoidal drive.
- ③
-
Calculate the positioning time
[In the case of trapezoidal drive]
[In the case of triangular drive]
-
- VRmax
- Maximum Speed Calculated for Triangular Drive [mm/s]
- VR
- Operating Speed [mm/s]
- Vs
- Starting Speed [mm/s]
- L
- Positioning Distance [mm]
- a1
- Acceleration [m/s²]
- a2
- Deceleration [m/s²]
- T
- Positioning Time [s]
- T1
- Acceleration Time [s]
- T2
- Deceleration Time [s]
- T3
- Constant Speed Time [s]